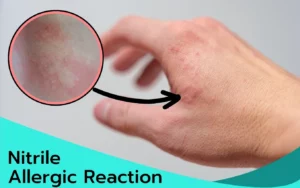
Reactions to nitrile gloves are generally less common than with latex gloves, but allergic responses can still occur. Symptoms of allergic contact dermatitis from nitrile gloves include redness, itching, and in severe cases, systemic reactions like breathing difficulties. This informative blog post examines into the prevalence, types of reactions, chemical sensitizers, diagnostic methods, and clinical cases related to nitrile allergic reactions. Whether you’re curious about nitrile allergy symptoms, testing methods, or preventive measures, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of nitrile allergic reactions for healthcare professionals and individuals alike.
Table of Contents
- Prevalence and Types of Reactions
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Delayed-Type Reactions
- Systemic Symptoms
- Chemical Sensitizers in Nitrile Gloves
- Ethyl Isothiocyanate (EITC) and Butyl Isothiocyanate (BITC)
- Zinc Diethyldithiocarbamate (ZDEC) and Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide (TETD)
- Other Potential Allergens
- Accelerator free disposable nitrile glove
- Diagnostic Methods
- Modified Skin Prick Tests
- Patch Tests
- Clinical Cases and Reports
- Contact Mucositis and Allergic Reactions
- Healthcare Settings and Nitrile Gloves
- Dental Implants and Titanium Nitride
- Occupational Contact Dermatitis
- Healthcare Workers and Dental Professionals
- Prolonged Use of Nitrile Gloves
- Chemical Permeation and Skin Reactions
- Contact Urticaria
- Immunological and Non-Immunological Reactions
- Unidentified Components in Nitrile Gloves
- Related Posts
Prevalence and Types of Reactions
While nitrile gloves are generally associated with fewer allergic reactions compared to latex gloves, it is important to understand the types of reactions that can occur. Most reactions to nitrile gloves are type IV hypersensitivity (delayed-type) rather than type I (immediate-type).
| Hypersensitivity Reactions: | Type IV hypersensitivity reactions are commonly seen with nitrile gloves, often presenting as erythema, itching, and localized rashes. |
| Delayed-Type Reactions: | Delayed-type reactions are more common with nitrile gloves and can manifest as contact dermatitis with symptoms like redness and itching appearing hours to days after exposure. |
| Systemic Symptoms: | Systemic symptoms, such as wheezing and breathlessness, can occur in severe cases of allergic reactions to nitrile gloves. |
Hypersensitivity Reactions
On the spectrum of allergic reactions to nitrile gloves, hypersensitivity reactions are primarily delayed-type responses that present with localized symptoms like itching and redness.
Delayed-Type Reactions
An examination of delayed-type reactions to nitrile gloves reveals that these responses often involve contact dermatitis, which can appear hours to days after exposure and may manifest as redness and itching on the skin.
Systemic Symptoms
An in-depth look at systemic symptoms associated with allergic reactions to nitrile gloves illustrates that in severe cases, individuals may experience symptoms like wheezing and breathlessness, indicating a more widespread and serious reaction.
Chemical Sensitizers in Nitrile Gloves

Ethyl Isothiocyanate (EITC) and Butyl Isothiocyanate (BITC)
Clearly, ethyl isothiocyanate (EITC) and butyl isothiocyanate (BITC) have been identified as potential allergens causing allergic reactions to nitrile gloves. These chemicals can lead to allergic contact dermatitis, manifesting as itching, erythema, and in severe cases, systemic symptoms like wheezing and breathlessness.
Zinc Diethyldithiocarbamate (ZDEC) and Tetraethylthiuram Disulfide (TETD)
On the other hand, zinc diethyldithiocarbamate (ZDEC) and tetraethylthiuram disulfide (TETD) are also known chemical accelerators in nitrile gloves associated with allergic contact dermatitis. These chemicals have been implicated in triggering adverse skin reactions and should be considered in cases of suspected nitrile glove allergies.
Other Potential Allergens
Tetraethylthiuram disulfide (TETD) is one of the other potential allergens found in nitrile gloves that can contribute to allergic reactions. Zinc diethyldithiocarbamate (ZDEC) is another chemical sensitizer that has been linked to allergic contact dermatitis in individuals using nitrile gloves. These chemicals highlight the importance of understanding the components of nitrile gloves to prevent and manage allergic reactions.
Accelerator free disposable nitrile glove
By eliminating these accelerators, the risk of allergic reactions and skin issues among users is significantly reduced. This is especially crucial in medical and surgical settings where skin sensitivity is a top concern.
The benefits of accelerator-free gloves extend beyond reduced allergic reactions. They also offer excellent chemical resistance, making them ideal for handling certain chemicals. While there may be some variability in chemical resistance among different nitrile gloves, accelerator-free options can provide consistent protection depending on their specific formulation. By choosing these hypoallergenic options, we can prioritize the well-being of users while maintaining a high level of protection and safety.
[tpgb-reusable id=”2147″]
Diagnostic Methods
Modified Skin Prick Tests
Unlike immediate hypersensitivity reactions seen with latex gloves, allergic reactions to nitrile gloves are primarily type IV delayed hypersensitivity. With modified skin prick tests, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose nitrile glove allergies by identifying both immediate and delayed contact dermatitis reactions.
Patch Tests
Prick Patch tests are effective tools for diagnosing allergic reactions to nitrile gloves. These tests involve applying small amounts of specific allergens (such as ethyl isothiocyanate and butyl isothiocyanate) onto the skin under occlusion and monitoring for any reactions. This helps differentiate between immunological and non-immunological responses, providing valuable insights into nitrile glove allergies.
Methods: Another diagnostic method for nitrile glove allergies is the patch test. In this test, various chemicals used in nitrile gloves, such as zinc diethyldithiocarbamate and tetraethylthiuram disulfide, are applied to the skin to observe for allergic reactions. This method helps in identifying specific chemical sensitizers causing allergic contact dermatitis in individuals sensitive to nitrile gloves.
Clinical Cases and Reports
Contact Mucositis and Allergic Reactions
The development of contact mucositis and other allergic reactions due to exposure to nitrile-coated materials, such as titanium nitride in dental implants, has been documented in clinical reports. This highlights the potential for nitrile gloves to trigger allergic reactions beyond skin contact.
Healthcare Settings and Nitrile Gloves
Allergic reactions to nitrile gloves are less common in healthcare settings compared to latex gloves, making them a preferred choice for professionals. Despite their hypoallergenic properties, some individuals may still experience allergic reactions to specific chemicals used in the manufacturing process.
Dental Implants and Titanium Nitride
Nitrile-coated materials, including titanium nitride used in dental implants, have been associated with allergic reactions, indicating a potential risk of sensitization to nitrile components in dental procedures. This awareness is crucial for ensuring patient safety and preventing adverse reactions in dental settings.
Occupational Contact Dermatitis
Healthcare Workers and Dental Professionals
Healthcare workers and dental professionals are particularly at risk of developing allergic contact dermatitis from prolonged use of nitrile gloves. Symptoms may include localized skin eruptions, itching, and redness. Despite the hypoallergenic properties of nitrile gloves, some individuals may still experience skin reactions due to specific chemicals used in their manufacturing process.
Prolonged Use of Nitrile Gloves
Gloves are important in healthcare settings where exposure to hazardous materials is frequent. However, prolonged use of nitrile gloves can lead to occupational contact dermatitis, especially in professions like healthcare and dentistry. It is crucial for individuals in these fields to be aware of the potential for allergic reactions and take preventive measures to protect their skin.
Chemical Permeation and Skin Reactions
Chemical permeation through nitrile gloves can contribute to skin reactions, particularly in healthcare settings where exposure to chemicals is high. Occupational contact dermatitis can occur when substances like 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) from dental adhesives pass through the gloves and come into contact with the skin. Proper glove usage and regular skin checks are important to prevent and manage these reactions.
Contact Urticaria
Immunological and Non-Immunological Reactions
Urticaria, also known as hives, can occur as a result of contact with certain components in nitrile gloves. This reaction may present as pruritic wheals and could be either immunological or non-immunological. Contact urticaria due to nitrile gloves is less common but has been reported, emphasizing the need for awareness of potential skin reactions.
Unidentified Components in Nitrile Gloves
With nitrile gloves, there is a possibility of experiencing allergic reactions to unidentified components present in the glove material. These unidentified components can trigger symptoms like erythema, itching, and contact urticaria, highlighting the complexity of nitrile glove allergies. While nitrile gloves are generally considered hypoallergenic, it is vital to consider the potential for reactions to unknown components.
So, while nitrile gloves are generally considered safer than latex gloves and are preferred for their durability and hypoallergenic properties, allergic reactions to nitrile gloves can still occur due to specific chemicals used in the manufacturing process. These reactions can manifest as contact dermatitis, urticaria, and in severe cases, systemic symptoms. It’s important for individuals, especially healthcare workers, to be aware of the potential for allergic reactions and take necessary precautions, including diagnostic testing to identify nitrile allergies.